 TarPmiR TarPmiR |
The identification of microRNA (miRNA) target sites is fundamentally important for studying gene regulation.
There are dozens of computational methods available for miRNA target site prediction. Despite their existence, we still cannot reliably identify miRNA target sites,
partially due to our limited understanding of the characteristics of miRNA target sites.
The recently published CLASH (cross-linking ligation and sequencing of hybrids) data provide an unprecedented opportunity to study the characteristics of miRNA target sites and improve miRNA target site prediction methods.
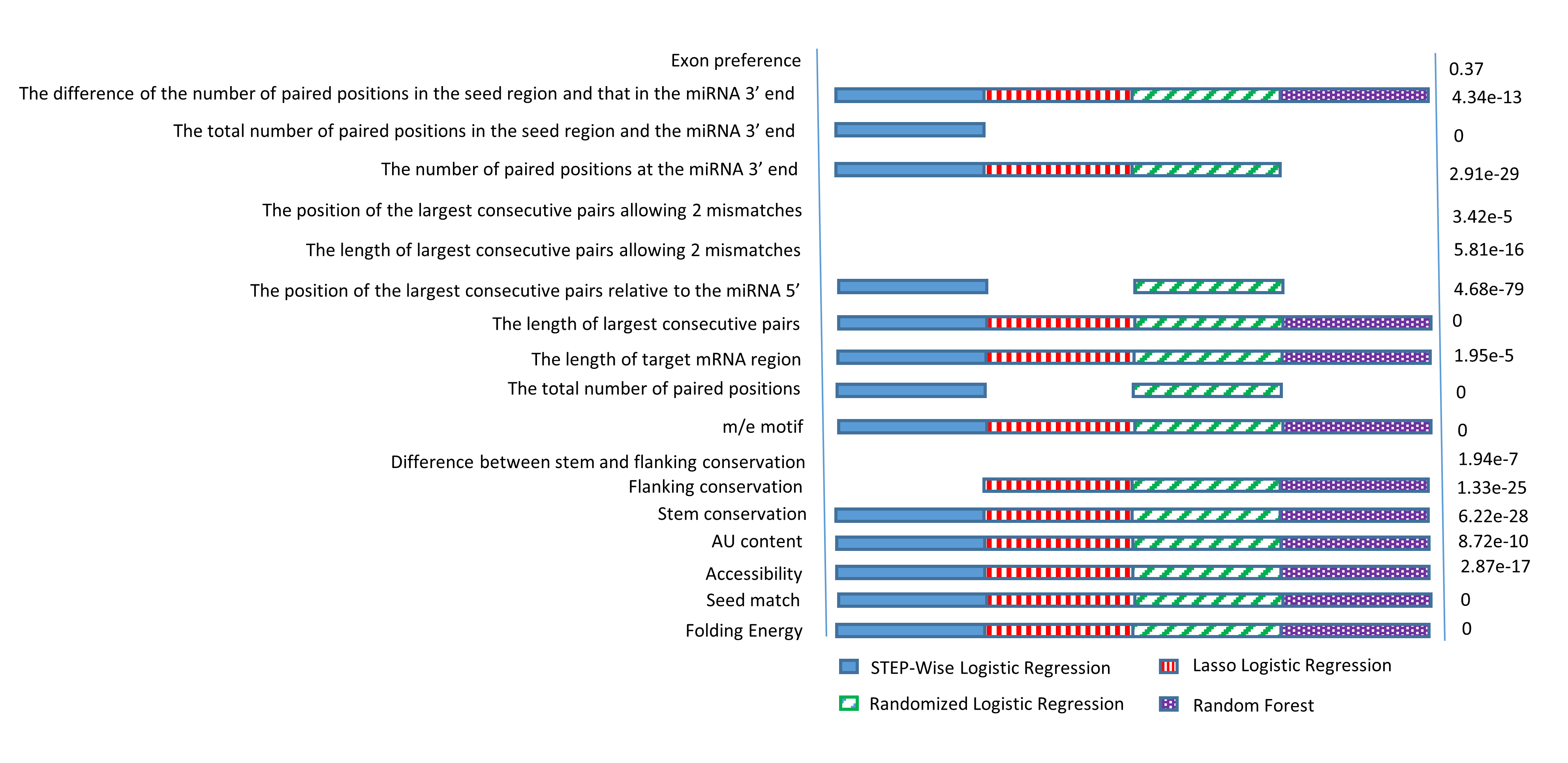
Applying four different machine learning approaches to the CLASH data, we identified seven new features of miRNA target sites.
Combining these new features with those commonly used by existing miRNA target prediction algorithms,
we developed an approach called TarPmiR for miRNA target site prediction. Testing on two human and one mouse non-CLASH datasets,
we showed that TarPmiR predicted more than 74.2 % of true miRNA target sites in each dataset. Compared with three existing approaches,
we demonstrated that TarPmiR is superior to these existing approaches in terms of better recall and better precision.
Although TarPmiR is based on the published CLASH data, users can easily apply TarPmiR to any new data set by extending the 'binding' class.
Please check 'How to extend TarPmiR' for more details.
 TarPmiR
TarPmiR  TarPmiR
TarPmiR 